29 May 2022, Mumbai:
Indian textile industry introduction
No gainsaying that the Indian textile industry is a critical contributor to the economy in terms of export earnings/FOREX & 2nd most significant employer. Albeit the nation is among the top exporters to the world, increasingly there is the unambiguous realization that the industry continues to be an underperformer to its underlying potential.
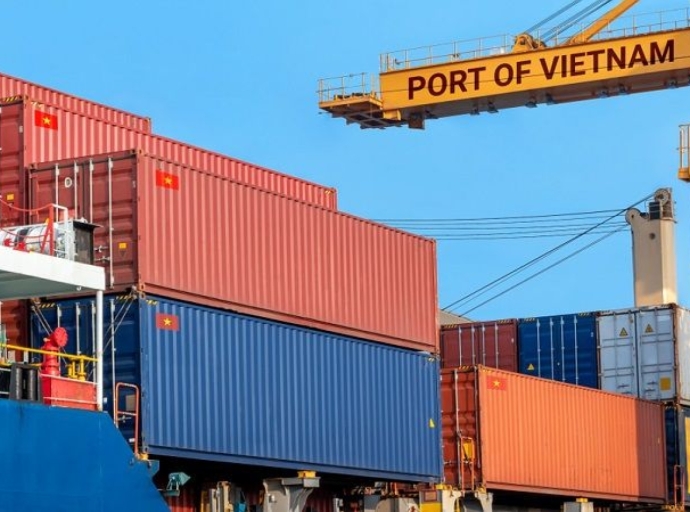
In India, textiles have a long history. India, long known as the land of exquisite fabrics, witnessed a fall in exports by 3% and 18.7% in 2020 whilst Other low-cost nations, such as Bangladesh and Vietnam, have gained market share.
Other low-cost nations, such as Bangladesh and Vietnam, have gained market share during the same period.
Indian textile industry history
Several variables have influenced India's recent trade performance. India suffers from several cost disadvantages. Exporters face pricing pressure due to a lack of free or preferential trade agreements with significant importers, such as the EU, UK, and Canada for garments and Bangladesh for textiles.
It's challenging to get the correct return on invested capital because of the high cost of capital and significant reliance on imports for practically all textile machines. India is uncompetitive in the fashion sector due to longer lead times than Chinese manufacturers. In western economies, the practice of nearshoring hasn't improved matters.
Most varieties of cotton yarns, woven cotton textiles, and cotton knit fabric might be imported duty-free from India from January 1 next year, citing the India-Asean free trade agreement.
As a result, India may become a stable supplier of cotton, yarn, and textiles to Vietnam.
How did the Indian textile industry get back its dominance
The Vietnam Cotton and Spinning Association (VCOSANguyen )'s Hong Giang said there was plenty of room for economic collaboration in yarn, cotton, and textiles between the two nations.
"Indian firms excel at producing cotton fabrics and materials. From the standpoint of the Vietnam Cotton and Spinning Association, we welcome Indian investment in the fabric industry.
Importers and buyers from Vietnam interested in sourcing from India may take advantage of a discounted accommodation and travel package by attending the expo in India, he added.
The event, organized by the Indian embassy in HCM City in collaboration with VCOSA, drew nine Indian enterprises and local firms to the 18th Vietnam International Textile and Garment Industry Exhibition in HCM City from November 21 to 24.
Cotton and man-made staple fibers are the most common textile items exported from India to Vietnam.
Indian textile industry in global market
Simultaneously, all yarns and textiles are valued at less than US $ 20 million. It demonstrates that Indian cloth makers are ignoring chances.
And this is despite numerous attempts at all levels, as many corporations have participated in sourcing events held in Ho Chi Minh City from time to time.
Trade between India and Vietnam in textiles through the years has grown significantly, but there is still huge untapped potential. China's vacating space in the global textile trade thus it has opened an opportunity window.
But the million-dollar question is, "Will Indian manufacturers eventually catch the boat".







_large.jpeg)